TKT, akü termal yönetimi çözümlerinde önde gelen küresel bir uzmandır. Elektrikli otobüsler için tasarlandı, elektrikli kamyonlar, elektrikli ağır ekipman, ve elektrikli tekneler. Birçok tanınmış küresel otomobil üreticisine güvenilir akülü sıvı soğutma sistemleri sağladık, BYD ve Tata Motors dahil, ömrünü uzatmaya yardımcı olmak, emniyet, ve elektrikli ticari araç çeşitleri.

kaldıraç kullanıyoruz 25 Ticari araçlarınızın performansını artırmak için araç termal yönetiminde uzun yıllara dayanan deneyim ve sektör lideri tasarım ve üretim yetenekleri. Akü termal yönetim ürünlerimiz, 10 kW, İçerisine kadar hassas sıcaklık kontrolü 0.5 derece, tak ve çalıştır tasarımı, ve OEM/ODM özelleştirmesi.

Elektrikli otobüs BTMS için özel olarak tasarlanmıştır, pil sıvı soğutma.
1. Soğutma kapasitesi: 10KW / 8KW / 5KW / 3KW
2. Gerilim Aralığı: DC 220V-750V
3. Özelleştirilmiş: Isıtma / OEM / Boyut
4. Avantajları: 0.5 ° hassas sıcaklık kontrolü. Tak ve çalıştır. Talih 500 tedarikçi.

Elektrikli kamyon BTMS için özel olarak tasarlanmıştır, pil sıvı soğutma.
1. Soğutma kapasitesi: 10KW / 5KW
2. Gerilim Aralığı: DC 220V-750V
3. Özelleştirilmiş: Isıtma / OEM / Boyut
4. Avantajları: 0.5 ° hassas sıcaklık kontrolü. Tak ve çalıştır. Talih 500 tedarikçi.

Ağır ekipman BTMS'si için özel olarak tasarlanmıştır, pil sıvı soğutma.
1. Soğutma kapasitesi: 10KW / 8KW / 5KW / 3KW
2. Gerilim Aralığı: DC 220V-750V
3. Özelleştirilmiş: Isıtma / OEM / Boyut
4. Avantajları: 0.5 ° hassas sıcaklık kontrolü. Tak ve çalıştır. Talih 500 tedarikçi.

Elektrikli denizcilik BTMS'si için özel olarak tasarlanmıştır, pil sıvı soğutma.
1. Soğutma kapasitesi: 10KW / 8KW / 5KW
2. Gerilim Aralığı: DC 220V-750V
3. Özelleştirilmiş: Isıtma / OEM / Boyut
4. Avantajları: 0.5 ° hassas sıcaklık kontrolü. Tak ve çalıştır. Talih 500 tedarikçi.
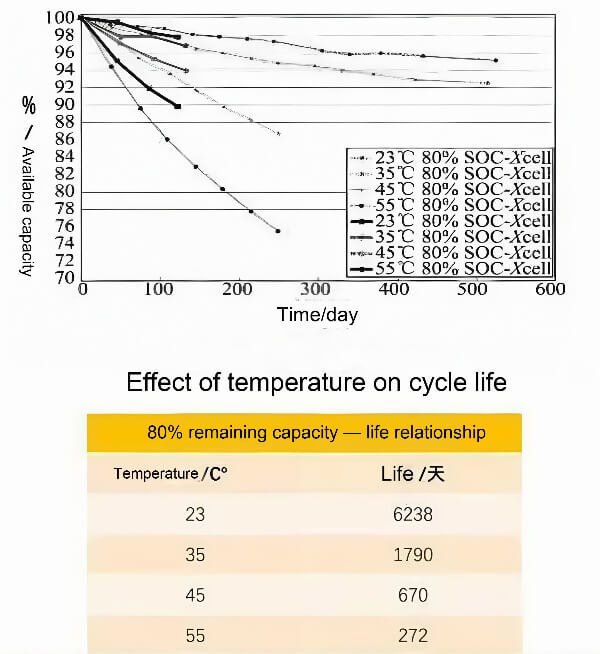
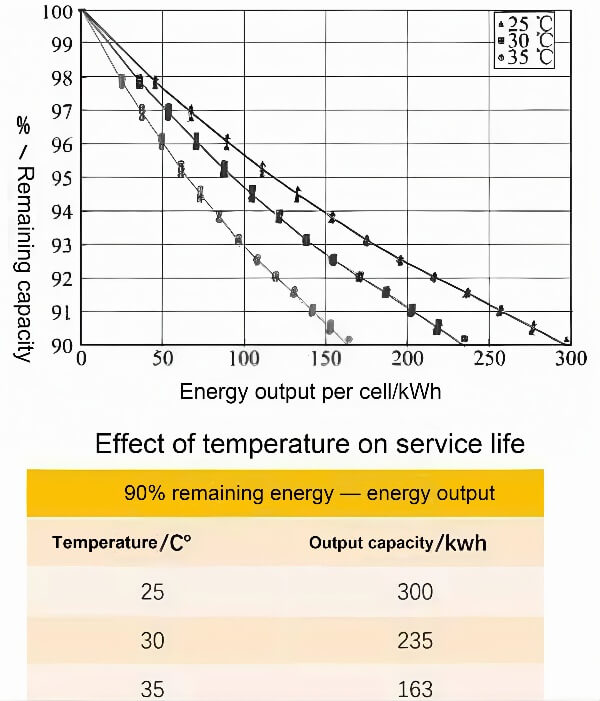
Pil termal yönetimi (BTM) Bir pil paketinin sıcaklığının, onu 10°C ila 45°C arasındaki ideal çalışma aralığında tutmak için aktif veya pasif olarak düzenlenmesini içerir. Daha gelişmiş teknik gereksinimler arasında, pil paketindeki her bir pil arasındaki sıcaklık farkının 5°C'nin altına düşürülmesi de yer alır.. Temel işlevleri arasında soğutma yer alır, ısıtma, ve sıcaklık dengeleme, Pil takımının çeşitli çevre koşullarında güvenli ve verimli çalışmasının sağlanması.
Temel hedefleri şunlardır::
1. Termal kaçakları önleyin: Zincir ekzotermik reaksiyonları tetikleyen yüksek sıcaklıklardan kaçının (yangın veya patlama gibi);
2. Pil performansını optimize edin: Deşarj kapasitesini artırmak için pil takımını düşük sıcaklıklarda ısıtın ve güç çıkışını korumak için yüksek sıcaklıklarda soğutun;
3. Pil ömrünü uzatın: Pilin bozulmasına neden olan sıcaklık dalgalanmalarını azaltın (lityum kaplama veya SEI filminin kalınlaştırılması gibi).
Güç pilleri elektrikli araçların enerji kaynağıdır. Şarj ve deşarj sırasında, pillerin kendisi önemli miktarda ısı üretir, sıcaklığın artmasına neden olur. Yüksek sıcaklıklar çeşitli pil özelliklerini etkileyebilir, iç direnç gibi, Gerilim, şarj durumu (Soc), Mevcut Kapasite, şarj/deşarj verimliliği, ve pil ömrü.
Akünün termal etkileri araç güvenliğini de etkiler, performans, ve pil çevrim ömrü. Bu noktalara ilerleyen bölümlerde değineceğim, bu yüzden lütfen okumaya devam edin. Öyleyse, Pil termal yönetimi son derece önemlidir.
Şu anda, EV akü termal yönetimi için en güvenilir ve pratik çözüm sıvı soğutma teknolojisidir. Açıklamak için örnek olarak sıvı soğutmayı kullanacağım.
1. Isı emilimi (akü → soğutma sıvısı)
Akü şarj ve deşarjı sırasında oluşan ısı, termal iletim yoluyla aküye temas eden sıvı soğutma plakasına aktarılır.. Soğutucu, sıvı soğutma plakasının içindeki mikro kanallardan akar, konvektif ısı değişimi yoluyla ısının emilmesi, soğutma suyu sıcaklığının yükselmesine neden olur.
2. Isı transferi (soğutma sıvısı → radyatör)
Isıtılan soğutma sıvısı bir elektrikli su pompası tarafından çalıştırılır ve borular aracılığıyla radyatöre taşınır.. Radyatör, basınçlı hava soğutması yoluyla ısıyı çevreye dağıtır., soğutucu sıcaklığının düşmesine neden olur.
3. Dolaşım
Soğutulan soğutucu sıvı soğutma plakasına geri döner, kapalı döngü dolaşımı oluşturmak.
Özetle, çalışma prensibi ısı iletimi ve konvektif ısı transferinin fiziksel mekanizmalarına dayanmaktadır., emilimin sağlanması, aktarma, ve akü ısısının kapalı devre soğutma sistemi aracılığıyla dağıtılması.
Genel olarak, iki ana tip var: aktif soğutma ve pasif soğutma. Temel fark, enerji tüketiminin gerçekleşip gerçekleşmeyeceğidir.. Enerji tüketimi meydana gelirse, aktif soğutmadır; sıfır enerji tüketimi varsa, pasif soğutmadır.
Aktif soğutma sistemi aşağıdakileri içerir::
1. Hava soğutmalı soğutma sistemi
Bu sistem öncelikle pil bölmesi içindeki havayı sirküle etmek için hava konveksiyonu prensibini kullanır.. Dolaşan hava akülerden ısıyı uzaklaştırır, böylece sıcaklıklarını düşürürler. Eşzamanlı olarak, hava, evaporatörde daha fazla ısı alışverişine uğrar, dolaşan havanın sıcaklığını azaltmak için soğutucunun buharlaştığı yer.Avantajları: Basit sistem yapısı, düşük maliyet, ve kolay bakım.
Dezavantajları: Yüksek sıcaklıkta zayıf ısı dağıtma performansı, düşük düşük sıcaklıkta başlatma verimliliği, ve piller arasında eşit olmayan stabilite.
2. Soğutucu doğrudan soğutma sistemi
Bu sistem öncelikle soğutucu akışkanların gizli buharlaşma ısısı ilkesinden yararlanır.. Akü sistemi içerisinde iklimlendirme sistemi kurulmuştur., akü sistemi içine monte edilmiş soğutma plakaları ile. Soğutucu akışkan soğutma plakaları içinde buharlaşır, Soğutmayı sağlamak için akü sistemindeki ısıyı hızlı ve verimli bir şekilde uzaklaştırır.
Avantajları: Basit yapı, teorik olarak düzgün sıcaklık dağılımı, ve iyi soğutma performansı;
Dezavantajları: Şu anda, teknoloji henüz olgunlaşmadı, ve kısa vadede ticarileştirilmesi pek mümkün görünmüyor.
3. Entegrasyon: Paylaşımlı Su Soğutmalı Soğutma Sistemi
Klima sistemine plakalı eşanjör eklenerek akuple edilmiştir.. Piller, soğutma plakaları aracılığıyla soğutucu ile ısı alışverişinde bulunur. Soğutulan veya ısıtılan soğutma sıvısı plakalı ısı eşanjörüne pompalanır., Soğutucu akışkanın bir tarafa aktığı ve soğutucu akışkanın diğer tarafa aktığı yer. Isı soğutucu tarafından uzaklaştırılır, ve soğutucu plakalı ısı eşanjöründen çıkıp akülere geri akar, döngüyü tamamlamak.
Avantajları: Kompakt yapı, entegre akü ısıtma bileşenleri, düşük sıcaklıkta yüksek başlatma verimliliği, mükemmel yüksek sıcaklıkta soğutma, ve düzgün sıcaklık dağılımı.
Dezavantajları: Çoklu sistem bileşenleri ve karmaşık kontrol stratejisi.
4 Bağımsız Batarya Sıvı Soğutma Sistemi
Pilin soğutulması gerektiğinde, soğutma plakası aracılığıyla soğutucuyla ısı alışverişi yapar. Isıtılan soğutma sıvısı, elektronik bir su pompası aracılığıyla plakalı ısı eşanjörüne pompalanır.. Plakalı eşanjörün içi, Soğutucu akışkan bir tarafa akar ve soğutucu akışkan diğer tarafa akar, ısı alışverişi nerede. Isı soğutucu tarafından uzaklaştırılır, ve soğutucu plakalı ısı eşanjöründen çıkıp aküye geri akar, döngüyü tamamlamak.
Pilin ısıtılması gerektiğinde, soğutma devresi kapatılır ve PTC sıvı ısıtıcısı etkinleştirilir. Isıtılan soğutma sıvısı daha sonra aküye beslenir, pili soğutma plakası aracılığıyla ısıttığı yer. Dahili akü sıcaklığı, soğutma devresi ve PTC sıvı ısıtıcısı kontrol edilerek kontrol edilir.
Avantajları: Kompakt yapı, entegre akü ısıtma bileşenleri, düşük sıcaklıkta yüksek başlatma verimliliği, mükemmel yüksek sıcaklıkta soğutma, ve düzgün sıcaklık dağılımı.
Dezavantajları: Çoklu sistem bileşenleri ve karmaşık kontrol stratejisi.
Bağımsız akülü sıvı soğutma sistemi bir kompresörden oluşur, yoğunlaştırıcı, genişleme subabı, plaka ısı eşanjörü, elektronik su pompası, PTC sıvı ısıtıcı, genişleme tankı, ve elektrik kontrolü.
Pasif soğutma sistemleri aşağıdakileri içerir::
1. Faz Değişim Malzemesi Akü Termal Yönetimi (PCM-BTM)
Bu sistem, faz değiştiren malzemelerin gizli ısı özelliklerinden yararlanır. (PCM'ler), katı-sıvı faz geçişleri yoluyla ısının emilmesi veya serbest bırakılması. Isıyı malzemenin fiziksel özellikleri yoluyla aktarır., Aktif soğutma sistemlerinin enerji tüketimini ortadan kaldırmak.
Avantajları: Enerji tüketimi yok, tutarlı sıcaklık.
Dezavantajları: Ağır ağırlık, kısa ömür.
2. Isı Borusu Teknolojisi
Isı borusu teknolojisi, ısı transferi için sıvılardaki faz değişiminden yararlanan yüksek verimli bir termal iletkenlik elemanıdır.. Bir tüp kabuğundan oluşur, bir fitil, ve uç kapakları. Tüpün içinde negatif bir basınç oluşturulur ve düşük kaynama noktalı bir sıvı ile doldurulur.. Bir ucu ısıtıldığında, sıvı buharlaşır ve buharlaşır. Buhar soğuk uca akar, ısının yoğunlaşması ve serbest bırakılması. Yoğunlaşan sıvı daha sonra kılcal hareket yoluyla buharlaşma ucuna geri akar., bir döngü oluşturmak.
Avantajları: Enerji tüketimi yok, düzgün sıcaklık.
Dezavantajları: Yüksek maliyet ve karmaşık tasarım. Öncelikle uzay aracı ekipmanlarında kullanılır.
| Soğutucu Tipi | Isı İletkenliği (W/m·K) | Özgül Isı Kapasitesi (kJ/kg·K) | Avantajları | Dezavantajları |
| Etilen glikol sulu çözeltisi | 0.4 | 3.5 | Antifriz, düşük maliyet | Yüksek viskozite, pompalama gücü, oksidasyon, asit üretimi, metal korozyonu |
| Florlu Sıvı | 0.07–0,08 | 1.1 | Yanıcı değildir, iyi yalıtım, aşındırıcı olmayan | Yüksek fiyat, yüksek GWP |
| Deiyonize su | 0.6 | 4.18 | Optimum termal iletkenlik, çevre dostu | Yüksek elektrik iletkenliği kısa devreye neden olabilir |
| Madeni yağ | 0.1–0,15 | 1.8 | İyi yalıtım, orta maliyet | Oksidasyona ve ayrışmaya duyarlı, yüksek viskozite, zayıf akışkanlık |
| Nanoakışkanlar | 0.5–0,8 | 2.2 | 40% daha yüksek termal iletkenlik, yüksek güç yoğunluğuna uygun | Son derece yüksek maliyet, parçacık çökelmesi riski |