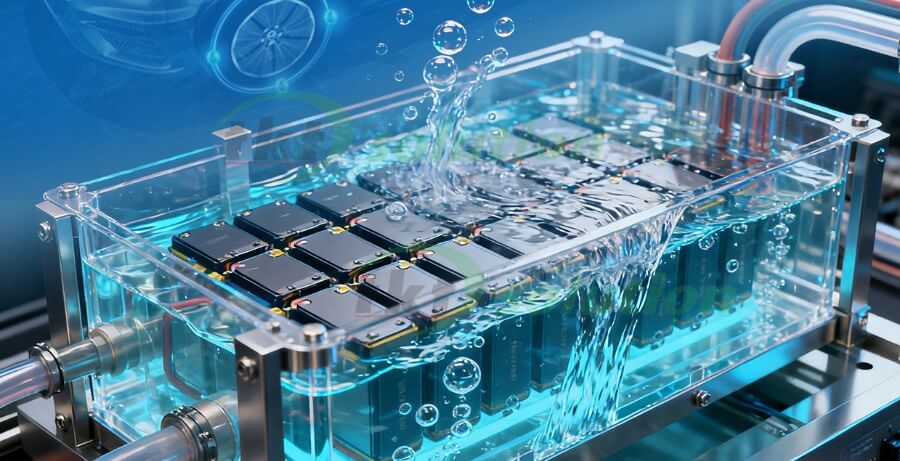
Battery immersion cooling is a battery thermal management approach that fully submerges the entire power battery pack in a non-conductive, non-flammable dielectric coolant. It eliminates liquid-cooled plate heat exchangers, instead achieving heat exchange through direct, maximum-surface-area contact between the battery and coolant. This leverages the liquid's high thermal conductivity and fluidity to rapidly absorb heat, thereby enabling more efficient battery temperature control.
Battery Immersion Cooling Schematic Diagram
Based on whether the coolant undergoes a phase change, it can be categorized into two types:
1. Single-phase Immersion Battery Cooling: Heat generated by the battery is absorbed by the surrounding coolant, which does not undergo a phase change (Ou seja,, remains liquid throughout). The heated coolant is circulated via an electric pump to an external heat exchanger, where heat is dissipated into ambient air or another liquid cooling system. After cooling, it recirculates back into the battery enclosure.
2. Two-phase Immersion Battery Cooling: Utilizes a special coolant with a low boiling point. When the battery generates heat, the coolant in contact absorbs the heat and undergoes a phase transition (Ou seja,, vaporizes into a gaseous state). This phase transition process absorbs a significant amount of heat with high efficiency. The resulting coolant vapor rises to a condenser at the top of the tank, where it reconverts to liquid and drips back down, completing a natural cycle. Characteristics: Extremely efficient thermal management without requiring pump operation. Por outro lado, the system demands higher standards for sealing integrity and pressure control, making it more technically complex and costly.
Core Advantages of Battery Immersion Cooling
1. Efficient Heat Dissipation: Liquid thermal conductivity is 5-10 times that of air, rapidly removing battery heat and suppressing temperature rise.
2. Excellent Temperature Uniformity: Liquid fully covers the battery surface, minimizing local hotspots. Tests show immersion cooling maintains maximum temperature differences within 1°C, compared to 3-5°C for cold plate liquid cooling. This is crucial for extending battery life and enhancing safety, potentially increasing lifespan by 10%-30%.
3. Enhanced Safety: The coolant possesses flame-retardant properties, isolates oxygen, rapidly absorbs heat during thermal runaway, and suppresses flame propagation, reducing fire probability by over 80%.
4. High Space Utilization: Eliminates cold plates, piping, and other structures, making it suitable for high-density battery layouts. Increases battery capacity by 20%-30% within the same volume.
Application Scenarios
1. High-Performance Electric Vehicles (VEs): The current solution remains in the proof-of-concept phase, primarily due to its high cost. The primary application being explored is high-performance racing, where thermal management and safety requirements outweigh cost considerations.
2. Energy Storage Systems (ESS): This represents the most promising application for battery immersion cooling. Large-scale energy storage facilities prioritize safety as their primary lifeline. Immersion cooling effectively resolves critical challenges in heat dissipation and thermal runaway propagation. Industry leaders like CATL and Tesla are actively developing and deploying related technologies.
3. Data Centers: In scenarios demanding extreme reliability, immersion cooling delivers a more stable and secure operational environment.
Is the battery immersion cooling system practical?
I've already touched on its core advantages earlier. It has achieved top-tier performance in heat dissipation rate, uniformidade de temperatura, segurança, and space utilization. No entanto, it remains in the demonstration application and early commercialization stages, lacking large-scale, long-term market validation. The three main issues are:
1. Custo extremamente alto, as the coolant itself is expensive.
2. Demanding system sealing requirements: It necessitates fully sealed battery packs, imposing stringent demands on materials and manufacturing processes.
3. Complex and challenging maintenance: Regular monitoring of coolant conditions requires specialized personnel. Adicionalmente, repair procedures and coolant replacement operations are highly intricate when issues arise.
Resumindo, battery immersion cooling is a technology with outstanding performance but incomplete conditions for widespread adoption. While it offers leading advantages in absolute performance and safety, its high cost and unresolved mass production challenges limit large-scale application. Consequentemente, it is not yet widely used in the commercial sector. The battery thermal management system currently widely used in the commercial sector is battery liquid cooling.
What is a battery liquid cooling system?
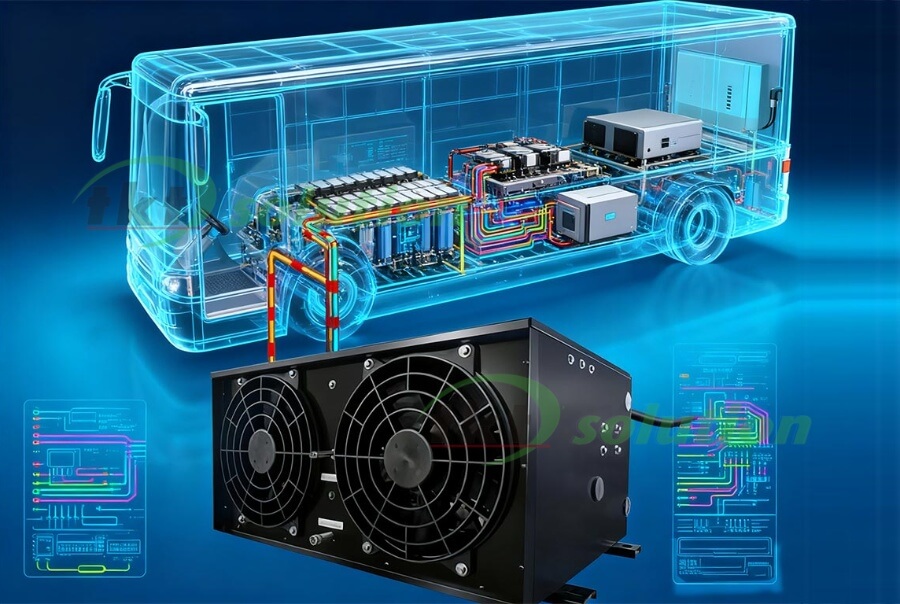
A sistema de refrigeração líquida da bateria circulates coolant through liquid cooling plates within the battery pack to absorb heat generated by the cells. This heat is then transferred to a radiator located at the front or side of the vehicle. The radiator subsequently exchanges heat with the outside air via fans. This constitutes a secondary heat exchange system.
Liquid cooling systems represent the most mature commercial option available today. They achieve the optimal balance across cost, confiabilidade, and safety. For the next 5-10 anos, they will remain the preferred choice for the majority of commercial electric vehicles.
TKT Sistema de refrigeração líquida de bateria
For a more intuitive comparison, I have compiled a detailed comparison table for you:
|
System Type |
Sistema de refrigeração líquida de bateria |
Battery Immersion Cooling System |
|
Princípio de funcionamento |
Indirect Cooling: Coolant flows through channels in the liquid cooling plate, exchanging heat with the battery via the metal plate. |
Direct Cooling: The battery is directly immersed in dielectric coolant, enabling maximum surface area heat exchange. |
|
Eficiência de resfriamento |
High, meeting the demands of most current electric vehicles. |
Exceptionally high, far surpassing liquid cooling. |
|
Temperature Uniformity |
Good, but slight temperature variations still exist across different areas of the cell. |
Excellent, with uniform cooling throughout the cell and minimal temperature differences. |
|
Segurança |
High: Relies on BMS and thermal runaway detection design. |
Extremely high: The coolant itself is non-flammable and effectively suppresses the spread of thermal runaway. |
|
System Complexity |
Moderate to High: Requires a complex system including a liquid cooling plate, bomba de água, tubing, radiador, etc.. |
Partially Simple, Partially Complex: Eliminates some components, but features complex sealing and external heat exchanger design. |
|
Cost |
Moderate: Mature technology, established supply chain, controllable costs. |
Very high: Expensive coolant, costly sealing processes, overall costs potentially several times higher than liquid cooling. |
|
Repairability |
Good: Established repair procedures and supply chain are in place. |
Poor: Repairs require handling coolant, involve complex procedures, and necessitate returning to the original manufacturer for service. |
|
Aplicativos primários |
Widely applied across nearly all sectors including passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles, and energy storage. |
High-performance vehicles and premium energy storage systems currently in demonstration phases. |
|
Technology Maturity |
Highly Mature: Validated through over a decade of large-scale market deployment. |
Early Stage: Transitioning from laboratory testing to demonstration applications, lacking long-term validation. |
Resumo
Immersion battery cooling is a forward-looking technology poised for the future, having reached the ceiling in terms of absolute performance and safety. No entanto, numerous challenges remain before its widespread adoption.
1. Significant reduction in costs for coolants and other materials.
2. Resolution of engineering challenges such as sealing technology and maintenance solutions.
3. Market validation testing feedback across diverse climatic conditions and road environments.
Once these hurdles are overcome, this technology will propel the new energy industry toward greater efficiency and safety. Let us look forward to the future together.

Leitura adicional: Sistema de gerenciamento térmico da bateria para veículos elétricos e duração da bateria, Análise do sistema de resfriamento de bateria para barramento elétrico, Sistema de resfriamento de líquidos da bateria - como funciona?
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/TKTHVAC/
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/tkt-hvac
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@TKTHVAC