Batterie-Wärmemanagementsystem
Elektrisch betriebene Klimaanlage
Motorbetriebene Klimaanlage
Ladegeräte für Elektrofahrzeuge

TKT ist ein weltweit führender Experte für Batterie-Wärmemanagementlösungen. Für elektrische Busse ausgelegt, Elektro-Lkw, elektrisches schweres Gerät, und Elektroboote. Wir haben viele namhafte globale Automobilhersteller mit zuverlässigen Batterieflüssigkeitskühlsystemen ausgestattet, einschließlich BYD und Tata Motors, hilft, die Lebensdauer zu verlängern, Sicherheit, und Angebot an elektrischen Nutzfahrzeugen.

Wir nutzen 25 Jahrelange Erfahrung im Fahrzeug-Wärmemanagement und branchenführende Design- und Fertigungskapazitäten zur Verbesserung der Leistung Ihrer Nutzfahrzeuge. Unsere Produkte für die thermische Bewirtschaftung der Batterie sind für ihre leistungsstarke Kühlleistung von bis zu 10 kW, präzise Temperaturkontrolle bis innen 0.5 Grad, Plug-and-Play-Design, und OEM/ODM-Anpassung.

Speziell für Elektrobus BTMS entwickelt, Batterieflüssigkeitskühlung.
1. Kühlkapazität: 10KW / 8KW / 5KW / 3KW
2. Spannungsbereich: DC 220V-750V
3. Maßgeschneidert: Heizung / OEM / Abmessungen
4. Vorteile: 0.5 ℃ präzise Temperaturregelung. Plug-and-Play. Vermögen 500 Anbieter.

Speziell für Elektro-Lkw BTMS entwickelt, Batterieflüssigkeitskühlung.
1. Kühlkapazität: 10KW / 5KW
2. Spannungsbereich: DC 220V-750V
3. Maßgeschneidert: Heizung / OEM / Abmessungen
4. Vorteile: 0.5 ℃ präzise Temperaturregelung. Plug-and-Play. Vermögen 500 Anbieter.

Speziell für Schwermaschinen-BTMS entwickelt, Batterieflüssigkeitskühlung.
1. Kühlkapazität: 10KW / 8KW / 5KW / 3KW
2. Spannungsbereich: DC 220V-750V
3. Maßgeschneidert: Heizung / OEM / Abmessungen
4. Vorteile: 0.5 ℃ präzise Temperaturregelung. Plug-and-Play. Vermögen 500 Anbieter.

Speziell für elektrische Marine-BTMS entwickelt, Batterieflüssigkeitskühlung.
1. Kühlkapazität: 10KW / 8KW / 5KW
2. Spannungsbereich: DC 220V-750V
3. Maßgeschneidert: Heizung / OEM / Abmessungen
4. Vorteile: 0.5 ℃ präzise Temperaturregelung. Plug-and-Play. Vermögen 500 Anbieter.
Thermalmanagement der Batterie (BTM) umfasst aktiv oder passiv die Temperatur eines Akkus, um sie im idealen Betriebsbereich von 10 ° C - 45 ° C aufrechtzuerhalten. Zu den anspruchsvolleren technischen Anforderungen gehört auch die Kontrolle des Temperaturunterschieds zwischen den einzelnen Batterien im Batteriepaket auf unter 5 °C. Zu den Kernfunktionen gehört das Abkühlen, Heizung, und Temperaturausgleich, Gewährleistung eines sicheren und effizienten Betriebs des Akkus unter verschiedenen Umgebungsbedingungen.
Seine Kernziele sind:
1. Thermals Ausreißer verhindern: Vermeiden Sie hohe Temperaturen, die exotherme Reaktionen auslösen, die Kettenreaktionen auslösen (wie Brände oder Explosionen);
2. Batterieleistung optimieren: Erhitzen Sie den Akku bei niedrigen Temperaturen, um die Ausleitungskapazität zu verbessern und sie bei hohen Temperaturen abzukühlen, um die Leistung aufrechtzuerhalten;
3. Batterielebensdauer verlängern: Reduzieren Sie die Temperaturschwankungen, die den Batterieverschlechterung verursachen (wie Lithiumbeschichtung oder Verdickung des SEI -Films).
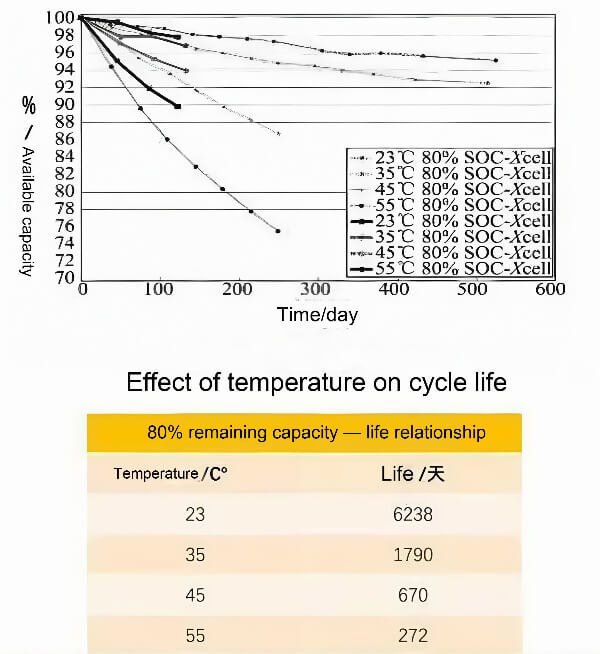
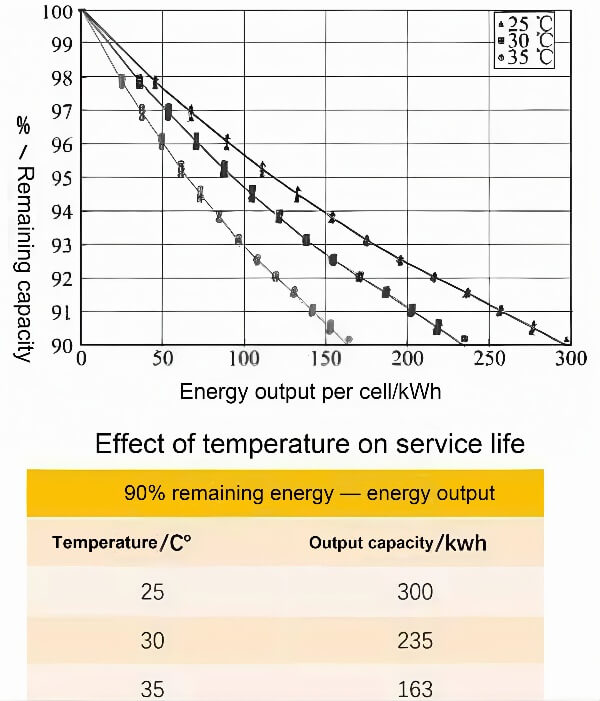
Strombatterien sind die Energiequelle für Elektrofahrzeuge. Während des Ladens und Entladens, Die Batterien selbst erzeugen eine erhebliche Menge an Wärme, was zu einem Temperaturanstieg führt. Erhöhte Temperaturen können verschiedene Batterieeigenschaften beeinflussen, wie zum Beispiel der innere Widerstand, Stromspannung, Gebührszustand (SOC), verfügbare Kapazität, Lade-/Entlassungseffizienz, und Batterielebensdauer.
Batterie -thermische Effekte beeinflussen auch die Fahrzeugsicherheit, Leistung, und Batteriezykluslebensdauer. Ich werde diese Punkte in den folgenden Abschnitten näher erläutern, Also bitte lesen Sie weiter. daher, Batterie -thermisches Management ist von größter Bedeutung.
Momentan, Die zuverlässigste und praktischste Lösung für das thermische Management der EV -Batterie ist die Flüssigkühlungstechnologie. Zur Erläuterung werde ich die Flüssigkeitskühlung als Beispiel verwenden.
1. Wärmeaufnahme (Batterie → Kühlmittel)
Die beim Laden und Entladen der Batterie entstehende Wärme wird über Wärmeleitung an die Flüssigkeitskühlplatte übertragen, die mit der Batterie in Kontakt steht. Das Kühlmittel fließt durch die Mikrokanäle im Inneren der Flüssigkeitskühlplatte, Aufnahme von Wärme durch konvektiven Wärmeaustausch, wodurch die Kühlmitteltemperatur ansteigt.
2. Wärmeübertragung (Kühlmittel → Kühler)
Das erwärmte Kühlmittel wird von einer elektrischen Wasserpumpe angetrieben und durch Rohre zum Kühler transportiert. Der Kühler gibt die Wärme durch forcierte Luftkühlung an die Umgebung ab, Dadurch sinkt die Kühlmitteltemperatur.
3. Verkehr
Das abgekühlte Kühlmittel kehrt zur Flüssigkeitskühlplatte zurück, eine Zirkulation mit geschlossenem Schleife bilden.
Zusammenfassend, Sein Betriebsprinzip basiert auf den physikalischen Mechanismen der Wärmeleitung und der konvektiven Wärmeübertragung, die Absorption erreichen, überweisen, und Dissipation der Batteriewärme durch ein Kühlmittelsystem mit geschlossenem Schleife.
Allgemein, Es gibt zwei Haupttypen: aktive Kühlung und passive Kühlung. Der Hauptunterschied besteht darin, ob Energieverbrauch entsteht. Wenn Energieverbrauch auftritt, es handelt sich um eine aktive Kühlung; wenn kein Energieverbrauch vorliegt, es handelt sich um eine passive Kühlung.
Das aktive Kühlsystem umfasst Folgendes:
1. Luftgekühltes Kühlsystem
Dieses System nutzt in erster Linie das Prinzip der Luftkonvektion, um die Luft im Batteriefach zu zirkulieren. Die zirkulierende Luft transportiert die Wärme von den Batterien ab, Dadurch wird ihre Temperatur gesenkt. Gleichzeitig, Die Luft erfährt im Verdampfer einen weiteren Wärmeaustausch, wo das Kältemittel verdampft, um die Temperatur der zirkulierenden Luft zu senken.Vorteile: Einfache Systemstruktur, niedrige Kosten, und einfache Wartung.
Nachteile: Schlechte Wärmeableitungsleistung bei hohen Temperaturen, niedrige Starteffizienz bei niedrigen Temperaturen, und ungleichmäßige Stabilität zwischen den Batterien.
2. Kältemittel-Direktkühlsystem
Dieses System nutzt in erster Linie das Prinzip der latenten Verdampfungswärme von Kältemitteln. Ein Klimaanlagensystem wird innerhalb des Batteriesystems festgelegt, mit Kühlplatten im Batteriesystem installiert. Kältemittel verdunstet innerhalb der Kühlplatten, schnell und effizient Wärme aus dem Batteriesystem entfernen, um Abkühlung zu erzielen.
Vorteile: Einfache Struktur, theoretisch gleichmäßige Temperaturverteilung, und gute Kühlleistung;
Nachteile: Momentan, Die Technologie ist noch nicht ausgereift, und eine Kommerzialisierung ist kurzfristig unwahrscheinlich.
3. Integration: Gemeinsames wassergekühltes Kühlsystem
Ein Plattenwärmetauscher wird hinzugefügt und an die Klimaanlage gekoppelt. Über die Kühlplatten tauschen die Batterien Wärme mit dem Kühlmittel aus. Das abgekühlte oder erwärmte Kühlmittel wird in den Plattenwärmetauscher gepumpt, Dabei strömt Kältemittel auf die eine Seite und Kühlmittel auf die andere. Die Wärme wird durch das Kältemittel abgeführt, und das Kühlmittel fließt aus dem Plattenwärmetauscher zurück in die Batterien, Abschluss des Zyklus.
Vorteile: Kompakte Struktur, Integrierte Batterieheizkomponenten, Hohe Starteffizienz bei niedrigen Temperaturen, hervorragende Hochtemperaturkühlung, und gleichmäßige Temperaturverteilung.
Nachteile: Mehrere Systemkomponenten und komplexe Steuerungsstrategie.
4 Unabhängiges Batterie-Flüssigkeitskühlsystem
Wenn die Batterie Kühlung benötigt, Es tauscht über die Kühlplatte Wärme mit dem Kühlmittel aus. Das erwärmte Kühlmittel wird von einer elektronischen Wasserpumpe in den Plattenwärmetauscher gepumpt. Im Plattenwärmetauscher, Auf der einen Seite strömt Kältemittel und auf der anderen Seite Kühlmittel, wo Wärme ausgetauscht wird. Die Wärme wird durch das Kältemittel abgeführt, und das Kühlmittel fließt aus dem Plattenwärmetauscher zurück in die Batterie, Abschluss des Zyklus.
Wenn die Batterie erwärmt werden muss, Der Kühlkreislauf wird geschlossen und die PTC-Flüssigkeitsheizung aktiviert. Das erwärmte Kühlmittel wird dann in die Batterie geleitet, Dort erwärmt es die Batterie durch die Kühlplatte. Die interne Batterietemperatur wird durch die Steuerung des Kühlkreislaufs und der PTC-Flüssigkeitsheizung geregelt.
Vorteile: Kompakte Struktur, Integrierte Batterieheizkomponenten, hohe Starteffizienz bei niedrigen Temperaturen, hervorragende Hochtemperaturkühlung, und gleichmäßige Temperaturverteilung.
Nachteile: Mehrere Systemkomponenten und komplexe Steuerungsstrategie.
Das unabhängige Batterieflüssigkeitskühlsystem besteht aus einem Kompressor, Kondensator, Expansionsventil, Plattenwärmetauscher, elektronische Wasserpumpe, PTC-Flüssigkeitserhitzer, Ausdehnungsgefäß, und elektrische Steuerung.
Passive Kühlsysteme umfassen Folgendes:
1. Wärmemanagement der Batterie mit Phasenwechselmaterial (PCM-BTM)
Dieses System nutzt die latenten Wärmeeigenschaften von Phasenwechselmaterialien (PCMs), Aufnahme oder Abgabe von Wärme durch Fest-Flüssig-Phasenübergänge. Es überträgt Wärme durch die physikalischen Eigenschaften des Materials, Eliminierung des Energieverbrauchs aktiver Kühlsysteme.
Vorteile: Kein Energieverbrauch, konstante Temperatur.
Nachteile: Schweres Gewicht, kurze Lebensdauer.
2. Heatpipe-Technologie
Bei der Heatpipe-Technologie handelt es sich um ein hocheffizientes Wärmeleitelement, das den Phasenwechsel in Flüssigkeiten zur Wärmeübertragung nutzt. Es besteht aus einer Rohrschale, ein Docht, und Endkappen. Im Inneren des Rohres wird ein Unterdruck erzeugt und es wird mit einer Flüssigkeit mit niedrigem Siedepunkt gefüllt. Wenn ein Ende erhitzt wird, die Flüssigkeit verdunstet und verdampft. Der Dampf strömt zum kalten Ende, kondensieren und Wärme abgeben. Die kondensierte Flüssigkeit fließt dann durch Kapillarwirkung zurück zum Verdampfungsende, einen Zyklus bilden.
Vorteile: Kein Energieverbrauch, gleichmäßige Temperatur.
Nachteile: Hohe Kosten und komplexes Design. Es wird hauptsächlich in der Ausrüstung von Raumfahrzeugen verwendet.
| Kühlmitteltyp | Wärmeleitfähigkeit (W/m·K) | Spezifische Wärmekapazität (kJ/kg·K) | Vorteile | Nachteile |
| Wässrige Ethylenglykollösung | 0.4 | 3.5 | Frostschutzmittel, niedrige Kosten | Hohe Viskosität, Pumpleistung, Oxidation, Säurebildung, Metallkorrosion |
| Fluorierte Flüssigkeit | 0.07–0,08 | 1.1 | Nicht brennbar, gute Isolierung, nicht korrodierend | Hohe Kosten, hohes GWP |
| Entionisiertes Wasser | 0.6 | 4.18 | Optimale Wärmeleitfähigkeit, umweltfreundlich | Eine hohe elektrische Leitfähigkeit kann zu Kurzschlüssen führen |
| Mineralöl | 0.1–0,15 | 1.8 | Gute Isolierung, moderate Kosten | Anfällig für Oxidation und Zersetzung, hohe Viskosität, schlechte Fließfähigkeit |
| Nanoflüssigkeiten | 0.5–0,8 | 2.2 | 40% höhere Wärmeleitfähigkeit, geeignet für hohe Leistungsdichte | Extrem hohe Kosten, Gefahr der Partikelablagerung |