TKT는 배터리 열 관리 솔루션 분야의 선도적인 글로벌 전문가입니다.. 전기 버스 용으로 설계되었습니다, 전기 트럭, 전기 중장비, 그리고 전기보트. 우리는 많은 유명 글로벌 자동차 제조업체에 안정적인 배터리 액체 냉각 시스템을 제공했습니다., BYD 및 Tata Motors 포함, 수명 연장에 도움, 안전, 다양한 전기 상용차.

우리는 활용한다 25 차량 열 관리 분야에서 다년간의 경험과 업계 최고의 설계 및 제조 역량을 통해 상용차의 성능을 향상시킵니다.. 우리의 배터리 열 관리 제품은 최대의 강력한 냉각 성능으로 유명합니다. 10 kW, 내부의 정확한 온도 제어 0.5 도, 플러그 앤 플레이 디자인, 및 OEM/ODM 맞춤화.
배터리 열 관리 (BTM) 배터리 팩의 온도를 적극적으로 또는 수동적으로 조절하여 10 ° C – 45 ° C의 이상적인 작동 범위 내에서 유지합니다.. 더욱 발전된 기술 요구 사항에는 배터리 팩에 포함된 각 배터리 간의 온도 차이를 5°C 미만으로 제어하는 것도 포함됩니다.. 핵심 기능에는 냉각이 포함됩니다, 난방, 그리고 온도 균형, 다양한 환경 조건에서 배터리 팩의 안전하고 효율적인 작동 보장.
핵심 목표입니다:
1. 열 런 어웨이를 방지하십시오: 체인 발열 반응을 유발하는 고온을 피하십시오 (화재 또는 폭발과 같은);
2. 배터리 성능을 최적화합니다: 배터리 팩을 저온에서 가열하여 방전 용량을 향상시키고 고온에서 식별하여 전력 출력을 유지하십시오.;
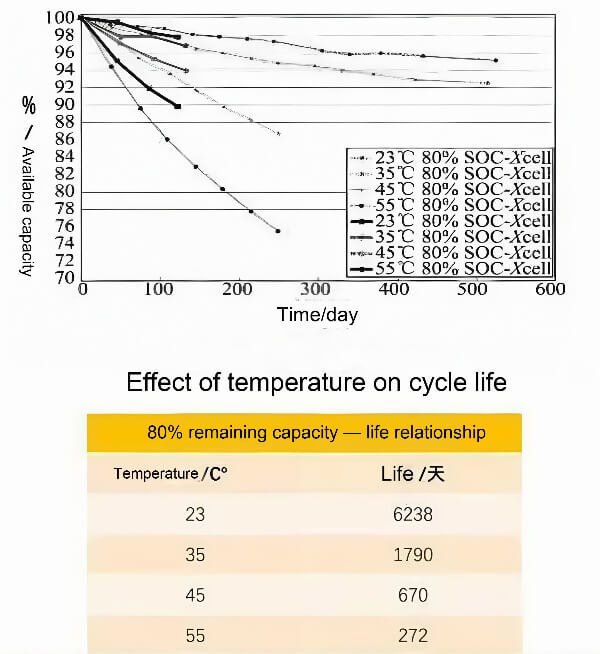
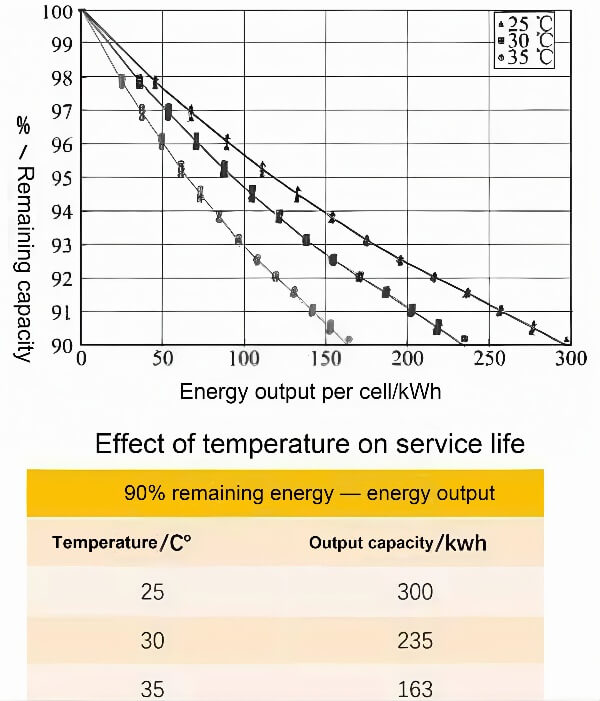
3. 배터리 수명을 연장하십시오: 배터리 분해를 일으키는 온도 변동을 줄입니다 (SEI 필름의 리튬 도금 또는 두껍게하는 것과 같은).
전원 배터리는 전기 자동차의 에너지 원입니다. 충전 및 배출 중, 배터리 자체는 상당한 양의 열을 생성합니다, 온도가 증가합니다. 온도가 높으면 다양한 배터리 특성에 영향을 줄 수 있습니다, 내부 저항과 같은, 전압, 요금 상태 (SOC), 사용 가능한 용량, 충전/배출 효율, 그리고 배터리 수명.
배터리 열 효과는 차량 안전에도 영향을 미칩니다, 성능, 그리고 배터리주기 수명. 다음 섹션 에서이 점에 대해 자세히 설명하겠습니다., 그러니 계속 읽으십시오. 그러므로, 배터리 열 관리가 가장 중요합니다.
현재, EV 배터리 열 관리를위한 가장 신뢰할 수 있고 실용적인 솔루션은 액체 냉각 기술입니다.. 나는 액체 냉각을 사용하여 설명 할 것이다..
1. 열 흡수 (배터리 → 냉각수)
배터리 충전 및 방전 중에 생성 된 열은 열 전도를 통해 배터리와 접촉하여 액체 냉각 플레이트로 옮겨집니다.. 냉각수는 액체 냉각 플레이트 내부의 마이크로 채널을 통해 흐릅니다., 대류 열 교환을 통한 열 흡수, 냉각수 온도가 상승합니다.
2. 열 전달 (냉각수 → 라디에이터)
가열 냉각수는 전기 워터 펌프에 의해 구동되고 파이프를 통해 라디에이터로 운반됩니다.. 라디에이터는 강제 공기 냉각을 통해 열을 환경으로 소실시킵니다., 냉각수 온도가 감소합니다.
3. 순환
냉각 된 냉각수는 액체 냉각 플레이트로 돌아갑니다, 폐 루프 순환 형성.
요약하자면, 작동 원리는 열 전도 및 대류 열 전달의 물리적 메커니즘을 기반으로합니다., 흡수 달성, 옮기다, 폐 루프 냉각수 시스템을 통한 배터리 열 소산.
일반적으로, 두 가지 주요 유형이 있습니다: 활성 냉각 및 수동 냉각. 주요 차이점은 에너지 소비가 발생하는지 여부입니다. 에너지 소비가 발생하는 경우, 활성 냉각입니다; 에너지 소비가없는 경우, 수동 냉각입니다.
활성 냉각 시스템에는 다음이 포함됩니다:
1. 공냉식 냉각 시스템
이 시스템은 주로 공기 대류의 원리를 사용하여 배터리 실 내에서 공기를 순환합니다.. 순환 공기는 배터리에서 열이 나옵니다, 따라서 온도를 낮추십시오. 동시에, 공기는 증발기 내에서 추가 열 교환을 겪습니다, 냉매가 증발하여 순환 공기의 온도를 낮추는 곳. 장점: 간단한 시스템 구조, 저렴한 비용, 쉬운 유지 보수.
단점: 불쌍한 고온 열 소산 성능, 낮은 온도 시작 효율성, 배터리 간 안정성이 고르지 못함.
2. 냉매 직접 냉각 시스템
이 시스템은 주로 냉매의 증발 원리 원리를 사용합니다.. 배터리 시스템 내에 에어컨 시스템이 설립되었습니다., 배터리 시스템 내에 냉각 플레이트가 설치되어 있습니다. 냉각 플레이트 내에서 냉매가 증발합니다, 냉각을 달성하기 위해 배터리 시스템에서 열을 빠르고 효율적으로 제거합니다..
장점: 간단한 구조, 이론적으로 균일 한 온도 분포, 그리고 좋은 냉각 성능;
단점: 현재, 기술은 아직 성숙하지 않습니다, 단기간 상용화는 어려울 듯.
3. 완성: 공유 수냉식 냉각 시스템
판형 열교환기가 에어컨 시스템에 추가되어 연결됩니다.. 배터리는 냉각판을 통해 냉각수와 열을 교환합니다.. 냉각되거나 가열된 냉각수는 판형 열교환기로 펌핑됩니다., 한쪽으로 냉매가 흐르고 다른쪽으로 냉각수가 흐르는 곳. 냉매에 의해 열이 제거됩니다., 냉각수는 판형 열교환기에서 빠져나와 배터리로 다시 유입됩니다., 사이클을 완료합니다.
장점: 소형 구조, 통합 배터리 가열 구성 요소, 높은 저온 시동 효율, 우수한 고온 냉각, 균일 한 온도 분포.
단점: 다중 시스템 구성 요소 및 복잡한 제어 전략.
4 독립 배터리 액체 냉각 시스템
배터리 냉각이 필요한 경우, 그것은 냉각판을 통해 냉각수와 열을 교환합니다.. 가열 냉각수는 전자 워터 펌프에 의해 플레이트 열교환 기에 펌핑됩니다.. 판형열교환기 내부, 냉매는 한쪽으로 흐르고 냉각수는 다른쪽으로 흐릅니다., 열이 교환되는 곳. 냉매에 의해 열이 제거됩니다., 냉각수는 판형 열교환기에서 빠져나와 배터리로 다시 유입됩니다., 사이클을 완료합니다.
배터리에 가열이 필요할 때, 냉각 회로가 닫히고 PTC 액체 히터가 활성화됩니다.. 가열된 냉각수는 배터리로 공급됩니다., 냉각판을 통해 배터리를 가열하는 곳. 냉각 회로와 PTC 액체 히터를 제어하여 배터리 내부 온도를 제어합니다..
장점: 소형 구조, 통합 배터리 가열 구성 요소, 높은 저온 시동 효율, 우수한 고온 냉각, 균일 한 온도 분포.
단점: 다중 시스템 구성 요소 및 복잡한 제어 전략.
독립형 배터리 액체 냉각 시스템은 압축기로 구성됩니다., 콘덴서, 확장 밸브, 판형 열교환기, 전자 워터 펌프, PTC 액체 히터, 팽창 탱크, 및 전기 제어.
패시브 냉각 시스템에는 다음이 포함됩니다.:
1. 위상 교체 재료 배터리 열 관리 (PCM-BTM)
상변화물질의 잠열특성을 활용한 시스템입니다. (PCM), 고체-액체 상전이를 통해 열을 흡수하거나 방출. 물질의 물리적 특성을 통해 열을 전달합니다., 활성 냉각 시스템의 에너지 소비 제거.
장점: 에너지 소비가 없습니다, 일정한 온도.
단점: 무거운 중량, 짧은 수명.
2. 히트파이프 기술
히트파이프 기술은 열전달을 위해 액체의 상변화를 활용하는 고효율 열전도 요소입니다.. 튜브 쉘로 구성됩니다, 심지, 그리고 엔드 캡. 튜브 내부에 부압이 생기고 끓는점이 낮은 액체가 채워집니다.. 한쪽 끝이 가열되면, 액체가 증발하고 기화됩니다.. 증기는 차가운 끝으로 흐른다., 응축 및 열 방출. 응축된 액체는 모세관 작용을 통해 증발 끝부분으로 다시 흐릅니다., 사이클 형성.
장점: 에너지 소비가 없습니다, 균일한 온도.
단점: 높은 비용과 복잡한 디자인. 주로 우주선 장비에 사용됩니다..
| 절삭유 종류 | 열전도율 (W/m·K) | 비열 용량 (kJ/kg·K) | 장점 | 단점 |
| 에틸렌글리콜 수용액 | 0.4 | 3.5 | 부동액, 저렴한 비용 | 고점도, 펌핑 파워, 산화, 산 발생, 금속 부식 |
| 불소화 유체 | 0.07-0.08 | 1.1 | 불연성, 좋은 단열, 비부식성 | 고비용, 높은 GWP |
| 탈이온수 | 0.6 | 4.18 | 최적의 열전도율, 환경 친화적인 | 전기 전도성이 높으면 단락이 발생할 수 있습니다. |
| 미네랄 오일 | 0.1-0.15 | 1.8 | 좋은 단열, 적당한 비용 | 산화 및 분해되기 쉬움, 고점도, 유동성이 좋지 않음 |
| 나노유체 | 0.5-0.8 | 2.2 | 40% 더 높은 열전도율, 높은 전력 밀도에 적합 | 매우 높은 비용, 입자 침전 위험 |